中国科学院上海高等研究院(以下简称“高研院”)是由中国科学院和上海市人民政府共建的科研机构,坐落于中国科学院上海浦东科技园。高研院积极开展原始创新和集成创新研究,加强与海内外研发机构、大学和企业的合作,集聚海内外杰出学者,促进我国相关战略新兴产业发展成为技术引领者,加快科学技术成果转移转化。实践科技与经济、科技与教育、科技与金融、科技与文化的四结合,成为有国际竞争力的集研、产、学、用为一体的多学科交叉综合性科教机构,为国家和区域经济增长方式转变提供相关领域的技术支撑与决策支持。
高研院已形成交叉前沿与先进材料、信息科学与技术、空间科技、能源与环境、生命科学与技术及技术转移转化的“五部一中心”的发展格局。在未来五至十年,高研院将以先进微小卫星、绿色智能城网、高端医疗影像设备三个重大突破为目标,将物联网行业应用、无线三网融合、可持续能源解决方案、温室气体和环境工程、干细胞与纳米医学作为五个重点培育方向大力发展科研及其应用。
高研院正成为创新功能体系完善、人才队伍集聚、技术创新平台及基础设施先进、布局合理、设施一流、配套完善、环境优美、在国内外有影响的研究院,建立健全有利于创新的体制和机制,与上海科技大学共同打造人才培养和科技创新的生态系统。
振翅欲飞的高研院,正以海纳百川之胸怀、协力创新之精神,期待海内外人才的加入,愿我们携手将高研院建设成为具有国际竞争力的高技术研究机构,共创辉煌未来!
Jointly established by Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Shanghai Municipal Government officially launched in 2012 at the Zhangjiang High-tech Park, the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI-CAS) conducts innovative research in a broad range of scientific fields and aims to foster collaboration between academia and industry. By bringing together talents from different backgrounds, SARI-CAS is dedicated to providing effective solutions for sustainable development of the society.
SARI-CAS focuses on interdisciplinary research and technology incubation, with research areas in Space Technology, Information Technology, Energy and Environment, Frontier Studies and Advanced Manufacturing. Striving to become a comprehensive research and education institution that integrates research, industry and education together, SARI-CAS has made impressive progress in microsatellite, advanced medical equipment, tri-networks convergence, smart low carbon city, internet of things, carbon data evaluation, and energy conservation and emission reduction.
With the spirit of open for cooperation, SARI has established extensive partnerships with national and international partners and has incubated many start-up companies, including advanced medical equipment and IT solutions provider Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare and NEEQ-listed smart governmental services provider Shanghai Sarisoft Co., Ltd.
Facing a new historic opportunity, the CAS Leadership laid out the blueprint for the preparing of the Zhangjiang National Lab based on SARI, leveraging the major science and technology infrastructure cluster in Shanghai and integrating relevant research resources and advantages, aiming to play a key role in the construction of the Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Center and the Zhangjiang Integrated National Science Center.

上海光源科学中心:
上海光源(Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility,简称SSRF)是中国大陆第一台中能第三代同步辐射光源,坐落在浦东张江高科技园区,由国家发改委、中国科学院和上海市人民政府共同投资建设,于2004年12月25日开工建设,2009年4月29日竣工,5月6日正式对用户开放,总体性能位居国际先进水平。上海光源首批建成7条光束线站,2015年~2018年期间,“梦之线”、蛋白质设施5线6站、SiP·ME2研究平台等陆续建成,目前共有15条光束线19个实验站开放运行。上海光源具有波长范围宽、高强度、高亮度、高准直性、高偏振与准相干性、可准确计算、高稳定性等一系列比其他人工光源更优异的特性,可用以从事生命科学、材料科学、环境科学、信息科学、凝聚态物理、原子分子物理、团簇物理、化学、医学、药学、地质学等多学科的前沿基础研究,以及微电子、医药、石油、化工、生物工程、医疗诊断和微加工等高技术的开发应用的实验研究。
上海光源是国家重大创新能力基础设施,是支撑众多学科前沿基础研究、高新技术研发的大型综合性实验研究平台,向基础研究、应用研究、高新技术开发研究各领域的用户开放。上海应用物理研究所/上海光源国家科学中心(筹)负责装置的运行、维护和改进提高。
上海光源2009年5月6日正式对用户开放,除去集中维护检修期,每年向用户供光4000~5000小时。所有用户均可通过申请、审查、批准程序获得上海光源实验机时。
十年来,上海光源围绕科学前沿、国家重大需求与产业核心问题支撑用户开展创新研究,以工程建设、运行开放、关键技术研发和科学研究四位一体可持续发展的总思路,聚焦重大基础科学突破和关键核心技术发展,为广大用户提供了一个跨学科、综合性、多功能的大科学研究平台,在生命科学、凝聚态物理、材料科学、化学、能源与环境科学等多个学科前沿基础研究和高新技术研发领域产生了一批具有国际影响力的研究成果,有力地推动了相关学科的发展,成为我国科学家参与国际竞争的强大助力。同时,也进一步推动了我国包括同步辐射在内的大科学装置的发展。
SSRF(Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility) is one of the advanced third generation light sources in the world, and it supports and pushes the cutting-edge scientific research and the innovation in China.Since commencing operation in May 2009 the SSRF has provided bright x-ray beams to more than 10000 usersfrom universities, institutes, hospitals and high-tech companies from around the China and the world. Thefacility hasbeen used in many areas of scientific research and industrial development, including biology, physics, material science,chemistry, environmental science, archeology, biomedical applications, medicine and drug development, etc.Over 1900 publications have been generatedbased on the experiments conducted at the SSRF.The SSRF is also actively involved in the training and education of our next generation of scientists and engineers.The SSRF is committed to continuing to expand its capacity and strengthen its contribution to the cutting edge ofmodern science.

上海激光电子伽马源与中子源:
上海激光电子伽玛源(Shanghai Laser Electron Gamma Source-缩写为SLEGS,简称为激光伽玛)利用外部激光和上海光源(Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility-缩写为SSRF)储存环中的电子束通过康普顿散射产生伽玛光。SLEGS首期产生的伽玛光能量为0.4-20 MeV@CO2激光,覆盖了光核反应热点能区(keV到MeV),并且可连续或多个离散点调节,伽玛光通量将达到105-107 phs/s(全谱积分通量,分别对应20°-180°碰撞角度时的通量);利用准直器技术,能量分辨率好于5%,准直后通量约为全谱积分通量的85%以上,同时伽玛光斑可以实现F30mm以内的连续调节;伽玛光的发散度好于0.5 mrad。
SLEGS,利用上海光源储存环的高能电子和外部引入的CO2连续激光散射产生伽玛光。产生伽玛光的能量为0.4-20 MeV,并且可连续或多个离散点调节。其科学目标如下:通过光核反应开展核天体物理、核物理、极化物理等领域中的基础研究,特别是解决核物理、核天体物理中具有重大科学价值的问题;此外,还开展与航天、国防、核能等战略需求相关的应用基础研究,如利用伽玛射线开展航天电子元器件空间辐照效应中的总剂量效应、抗辐射加固评估研究,以及航天伽玛探测器的精确定标,核能关键反应截面测量,核废料嬗变机制研究等。建成的SLEGS装置有望成为一个开展基础物理和应用相结合的多功能实验平台。
表1光束线设计指标和验收指标
参数 |
设计指标 |
验收指标 |
能量范围 |
0.4-20 MeV |
0.4-20 MeV |
单色性 |
~5 %(加准直器) |
~5 %(加准直器) |
积分伽玛光通量 |
105phs/s@20°-107 phs/s@180° |
2×104phs/s@20°-2×106phs/s@180° |
发散度 |
<0.5 mrad |
<0.5 mrad |
SLEGS初期主要提供能量为0.4-20MeV的伽玛束,由斜入射产生,具有能量连续可调的特点,覆盖了核结构研究、核数据测量、核天体物理等当前基础研究领域的主要研究热点,以及广泛的应用研究目标。同时SLEGS设计方案中保留有180°背散射模式,通过更改激光器的波长(能量),例如由10.64μm更换为1064nm,532nm,355nm,266nm,同时对应更换相应的光学器件,即可实现更高伽玛能量的选择(例如20MeV - 700MeV范围),同时具有高极化度的康普顿背散射伽玛束流,提供更高能量和高极化度的选择,满足不同用户的研究目标和实验需求。这一目标可以在未来SLEGS装置的研究及扩展中实现。
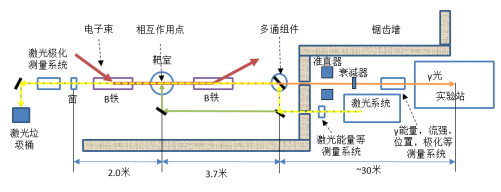
光中子源:
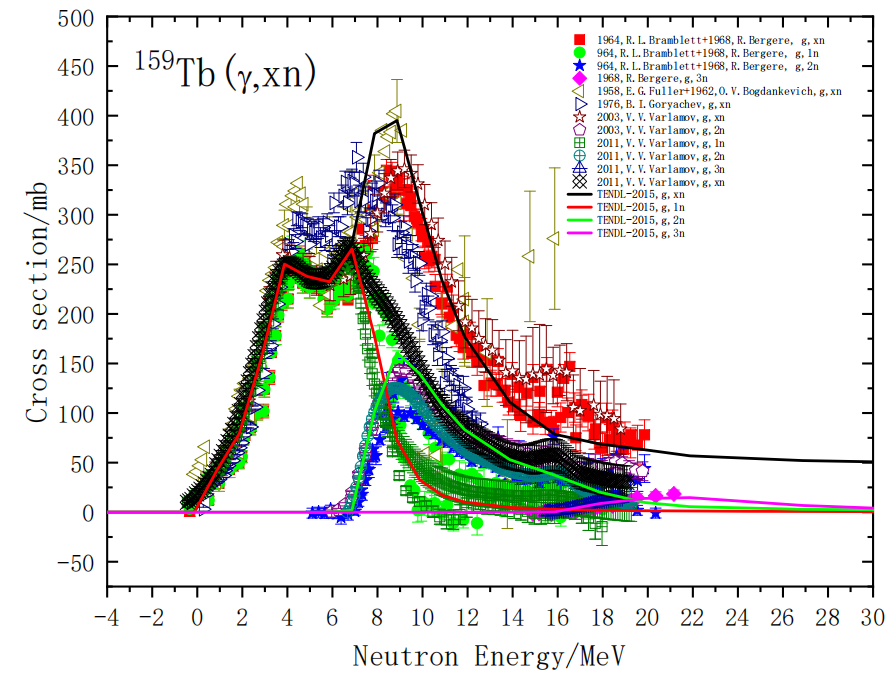
利用伽玛射线的光中子(g,n)反应道,即巨偶极共振GDR反应,未来我们可以获得可调能量的快中子束,如下图159Tb(g,xn)反应道所示,在中子发射阈值(Sn=8.133MeV)以上,光中子的截面最大,光中子能量主要集中在2-18MeV能区,通过调节伽玛射线的能量,可以得到不同锐截止边界的中子能谱。
Shanghai Laser Electron Gamma Source (SLEGS) @SSRF(Shanghai Light Source)
SLEGS is being constructed by combining SSRF storage ring’s electron and continuous-wave (CW) carbon dioxide (CO2) laser for gamma energy 0.4-20MeV. A new Compton backward Scattering facility will be proposed based on LINAC electron of the soft X-ray free electron laser (SXFEL@800MeV/1300MeV) and the super-intense ultrafast laser for high brightness gamma ray (3.7-38.9MeV) and peak brightness to 1021s.u.It will be expected to be constructed in 2020-2025.
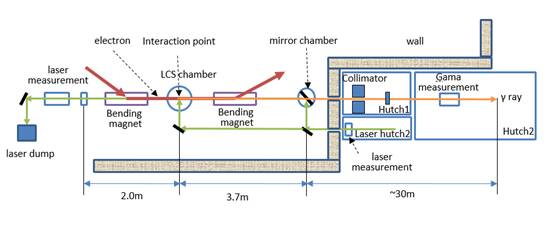
SLEGS beam station is one of the high quality gamma sources based on Laser Compton Scattering(LCS)at Shanghai Light source (Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility-SSRF). The energy region and flux of SLEGS are 0.4-20 MeV and 105-107phs/s, respectively. Based on the method of photonuclear reaction, SLEGS aims to nuclear structure researches such as Pigmy Dipole Resonance (PDR), Giant Dipole Resonance (GDR) and Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence (NRF), nuclear astrophysics, nuclear data measurement, polarization physics, and radiation physics. In addition, SLEGS also tends to carry out the applied research relating to aerospace, nuclear energy and other strategic demands of China, such as space radiation effect research of the aerospace electronic components, and accurate calibration of the gamma detector for aerospace.
The main facilities of SLEGS consist of interaction chamber in the storage ring of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), a laser system, and two experimental hutches. SLEGS has two operational modes: slanting-scattering mode (20°-160°) and backwardscattering mode (180°). In slanting-scattering mode, the γ-ray energy from 0.4 to 20 MeV can be produced by continuously changing the angle between the incident laser and the electron beam. Total photon flux can reach to 105-107 photons/second with acontinuous-wave(CW) carbon dioxide(CO2) laser. Combining with the lead collimator, the resolution of γ beamwill be better than 5%@2mm collimator.Meanwhile, the spot size can be adjusted from 0 to 20 mm continuously. In the backwardscattering mode, gamma-ray energy can reach 22 MeV with the flux of 107 photons/second and the polarization of gamma ray can reach to >95%.
As a beamline of SSRF phase II, SLEGS has been approved in the phase II project of SSRF. Design of SLEGS has been carried out in 2015. SLEGS will be constructed in the end of 2019-2020, and expected to be open for users from 2022.
Photo Neutron Source based on the SLEGS in future:PNS@SLEGS
Using the gamma-ray photo neutron (g,xn) reaction, i.e. the Giant Dipole Resonance(GDR) reaction region, in the future we can obtain a fast neutron beam of adjustable energy, as shown in the reaction in Figure 159Tb (g,xn), the largest cross-section of the photo neutron, above the neutron emission threshold (Sn=133MeV), The photo neutron energy is concentrated in the 2-18 MeV energy area, and by regulating the energy of gamma rays, the neutron energy spectrum of different sharp cut-off boundaries can be obtained in experiment.
王宏伟 研究员
中国科学院上海高等研究院
电话:13801818124
E-mail:wanghongwei@zjlab.org.cn

